The goose and the duck are both members of the waterfowl family and are often confused with each other. While they may look similar at first glance, there are several key differences between the two species. In this article, we will explore these differences in detail.
Physical Differences Between Geese and Ducks
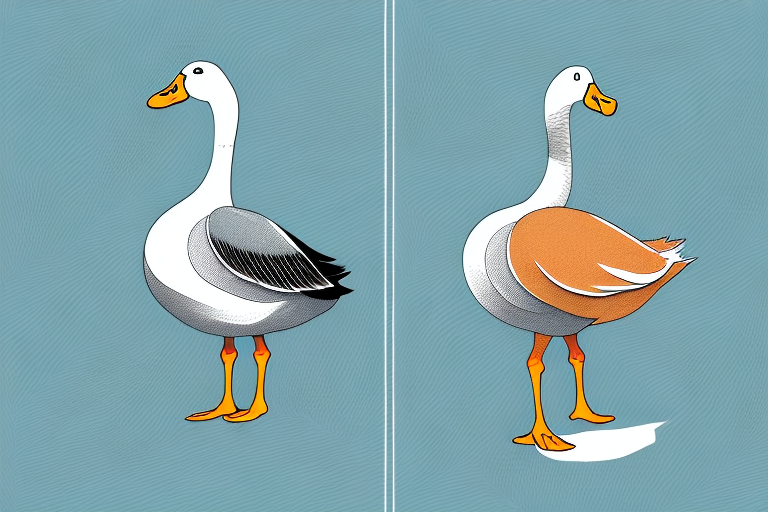
The first and most obvious difference between geese and ducks is their physical appearance. Geese are generally larger in size than ducks and have a longer neck as well. Their bodies are also wider and more robust, giving them a bulky appearance compared to the streamlined and sleek ducks. Additionally, geese have shorter wings and tails than ducks, as they are primarily land-based birds with limited flight capabilities.
Another key difference between geese and ducks is their beaks. Geese have a prominent, triangular-shaped beak that is designed for grazing on lush vegetation. Ducks, on the other hand, have a smaller and more rounded beak that is better suited for catching small fish and other aquatic prey. Their webbed feet also differ in shape, with geese having more pointed feet to grip the ground while ducks have rounder feet to help them swim smoothly in water.
One interesting fact about geese is that they are highly social birds and often travel in large flocks. They are known to mate for life and will fiercely protect their partners and offspring from any potential threats. Ducks, on the other hand, are more solitary creatures and tend to form smaller groups. They are also known for their unique courtship rituals, which involve elaborate displays of feathers and calls to attract a mate.
Behavioral Differences Between Geese and Ducks
In terms of behavior, geese tend to be more social and vocal than ducks. They are known for their loud honking calls that they use to communicate with each other, especially during migration. Geese also mate for life and are known to exhibit strong family bonds, with parents often taking turns to care for their young goslings.
Ducks, on the other hand, are more independent in nature and typically do not mate for life. They are known to form loose flocks during migration, and their communication is more subtle, with soft quacks and other low-pitched calls.
Another notable difference between geese and ducks is their feeding behavior. Geese are primarily grazers and feed on grasses, while ducks are dabblers and feed on aquatic plants and insects. This difference in feeding behavior also affects their habitat preferences, with geese preferring open grassy areas and ducks preferring wetlands and bodies of water.
Additionally, geese are known to be more aggressive than ducks, especially during breeding season. They will fiercely defend their nests and young from any perceived threats, including humans. Ducks, on the other hand, are generally more docile and less likely to attack humans or other animals.
Habitat Differences Between Geese and Ducks
Another key difference between geese and ducks is their habitat preference. Geese are primarily land-based birds and tend to live in open grassy areas near water bodies. They are commonly found in areas such as parks, golf courses, and farm fields. Ducks, on the other hand, are aquatic birds and prefer to live in or near water bodies. They can be found in a wide range of aquatic habitats, including ponds, lakes, rivers, and even coastal areas.
Geese are also known to be more territorial than ducks, and will often defend their nesting sites aggressively. They will even attack humans if they feel threatened. In contrast, ducks are generally more social and will often form large flocks, especially during migration season.
Another interesting difference between geese and ducks is their feeding behavior. Geese are primarily grazers and will feed on grasses and other vegetation found in their habitat. Ducks, on the other hand, are omnivores and will feed on a variety of foods, including insects, small fish, and aquatic plants. This difference in feeding behavior is also reflected in their beak structure, with geese having a broad, flat beak for grazing, and ducks having a narrow, pointed beak for catching prey.
Diet Differences Between Geese and Ducks
Geese are herbivores and primarily feed on grasses, grains, and other vegetation. They are known for their ability to graze on long and fibrous blades of grass, allowing them to extract the maximum amount of nutrients from their diet. Ducks are omnivores and have a more varied diet, which includes small fish, insects, and other aquatic creatures, along with vegetation. Their ability to dive and swim underwater allows them to access a wider range of prey compared to geese.
In addition to their different diets, geese and ducks also have different feeding behaviors. Geese are known for their grazing behavior, where they walk slowly and methodically while feeding on grass. They also have a unique digestive system that allows them to break down tough plant material, such as cellulose, which is not easily digestible by other animals. On the other hand, ducks are more active feeders and can often be seen diving and splashing in the water while feeding.
Another interesting difference between geese and ducks is their feeding patterns during migration. Geese are known for their long-distance migrations, where they fly in a V-formation and stop at various locations to feed and rest. During these stops, they often feed on agricultural crops such as corn and wheat. In contrast, ducks have shorter migration distances and tend to feed on natural food sources such as seeds, insects, and small aquatic animals along the way.
Reproduction Differences Between Geese and Ducks
Geese are known to be monogamous and typically mate for life. The mating season for geese is in the spring when they establish breeding territories and construct nests on the ground. The female lays a clutch of eggs, which both parents take turns incubating and protecting until they hatch.
Ducks, on the other hand, are more promiscuous and do not form long-term bonds with their partners. They typically breed during the spring and summer months and lay their eggs in nests near water bodies. The incubation period for duck eggs is short, typically lasting around a month, and the young ducklings are able to swim and feed themselves shortly after hatching.
Another notable difference between geese and ducks is their reproductive behavior in terms of flock size. Geese tend to breed in smaller flocks, with only a few pairs nesting in a particular area. In contrast, ducks often breed in larger flocks, with multiple males competing for the attention of a single female. This can lead to intense mating displays and fights among the males, as they try to establish dominance and win the right to mate with the female.
Economic Importance of Geese and Ducks
Geese and ducks are economically important birds that are widely consumed for their meat and eggs. They are also bred for their feathers, which are used in making down comforters, pillows, and jackets. Additionally, geese and ducks are popular game birds and are hunted for sport and recreation in many countries. In terms of agriculture, geese are known for their ability to control pests and weeds, making them an important asset for farmers.
Furthermore, geese and ducks are also important indicators of the health of wetland ecosystems. As waterfowl, they rely on wetlands for their survival and are sensitive to changes in water quality and habitat. By monitoring the populations and behaviors of geese and ducks, scientists can gain valuable insights into the health of wetland ecosystems and make informed decisions about conservation efforts.
Conservation Efforts for Geese and Ducks
Both geese and ducks are facing environmental threats such as habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. As a result, many conservation efforts are being undertaken to protect these birds and their habitats. These efforts range from habitat restoration to creating protected areas for breeding and migration. Additionally, hunting regulations have been put in place to ensure that these birds are not over-harvested and that their populations can thrive in the wild.
One specific conservation effort for geese and ducks is the use of artificial nesting structures. These structures mimic natural nesting sites and provide a safe place for birds to lay their eggs and raise their young. This is especially important in areas where natural nesting sites have been destroyed or are limited. The use of these structures has been successful in increasing the populations of certain species of geese and ducks.
Myth-busting: Common Misconceptions about Geese and Ducks
There are several common misconceptions about geese and ducks that have persisted over time. One of the most prominent myths is that feeding bread to ducks and geese is a harmless and fun activity. In reality, feeding ducks and geese bread can be harmful to their health and can lead to malnutrition and other health problems. Another myth is that geese and ducks have no purpose other than being pests or game birds. In reality, these birds have ecological and economic importance, playing a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting the livelihoods of many communities around the world.
Another common misconception about geese and ducks is that they are dirty animals. While it is true that they can leave droppings in public areas, this does not necessarily make them dirty. In fact, geese and ducks are very clean animals that spend a lot of time preening and grooming themselves. They also help to keep waterways clean by eating algae and other aquatic plants that can cause problems if left unchecked.
Additionally, some people believe that geese and ducks are aggressive and dangerous animals. While it is true that they can become territorial during breeding season, they are generally not aggressive towards humans unless they feel threatened or provoked. In fact, many people find these birds to be quite friendly and enjoy feeding them in a responsible manner, such as with birdseed or cracked corn.
Conclusion
In summary, while geese and ducks may be similar in some ways, there are several key differences that distinguish them from each other. These differences are not just physical, but also behavioral, ecological, and cultural. Understanding these differences is important for conserving these birds and their habitats, as well as appreciating the unique roles that each species plays in our world.